 It is so vital to turn and position patients while they are hospitalized either long-term stays or short-term patients. The practice of regularly turning and positioning patients might seem straightforward, but it is essential of effective healthcare, especially for those who are bedridden or have mobility issues. It provides comfort and enhances health benefits.
It is so vital to turn and position patients while they are hospitalized either long-term stays or short-term patients. The practice of regularly turning and positioning patients might seem straightforward, but it is essential of effective healthcare, especially for those who are bedridden or have mobility issues. It provides comfort and enhances health benefits.
So, which patient will be benefits the most from this practice? For patients who are bedridden or have limited mobility are particularly at risk as their inability to move around puts them in a vulnerable position. The are prone to a have complications if they stay in the same position for too long.
What kind of complications can these patients suffer? Bedsore, poor circulation, respiratory problems, muscle and joint health, comfort and well-being amongst others.
First are pressure ulcers, also known as bedsores, can develop. These are painful and can lead to infections as well as other severe health problems. Second issue is blood circulation, it can also be a big issue as limited movement often means poor blood flow, which can result in conditions like deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Respiratory problems are another risk. When patients lie in one position for too long, especially on their back, they can experience lung issues such as pneumonia. The lungs need room to expand and clear out secretions efficiently. What’s about muscle and joint health? Staying immobile for extended periods can cause stiffness, contractures, and even joint deformities. Furthermore, the discomfort and the constant restlessness patients feel when stuck in the same position can affect their mental state and overall well-being.
Therefore, turning and positioning patients regularly is a must have and a must-do in any quality healthcare setting. It is a proactive care aimed at preventing a multitude of problems before they develop.
Primary Health Benefits of Regular Turning and Positioning
There are many health benefits of regular turning and positioning patients as below:
Firstly, avoiding pressure ulcers is a major benefit when turning and positioning patients correctly. Pressure ulcers, or bedsores, develop from constant pressure on the skin and underlying tissues, often over bony areas like hips or heels. Regular repositioning relieves this pressure, making it a simple yet crucial step in preventing these painful sores.
Secondly, blood circulation sees a noticeable improvement too. When a patient stays in one position for too long, blood flow can get restricted, especially to the lower parts of the body. Regular movement promotes proper blood circulation, which is key to keeping tissues well-oxygenated and preventing problems like deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Thirdly, respiratory health benefits considerably from regular turning. Extended periods in one position, particularly on the back, can lead to lung issues due to fluid buildup and restricted lung expansion. Changing positions helps the lungs expand more effectively and clear out secretions, reducing the risk of pneumonia and other respiratory issues.
Lastly, muscle and joint health. There is also a positive impact on muscle and joint health. Staying immobile can cause muscles to stiffen and joints to become less flexible. Repositioning patients keeps muscles engaged and helps maintain joint flexibility and movement.
Additional Advantages for Patient Comfort and Well-being
Apart from these above benefits when turning and positioning patients, there are additional advantages such as patient comfort and well-being.
Increasing patient comfort is another huge benefit of regular turning and positioning as being stuck in one position for too long can cause serious discomfort and even pain. Repositioning alleviates this, making a big difference to how the patient feels day-to-day.
Swelling, especially in the lower limbs, can be a significant issue for patients with limited mobility. Poor circulation allows fluid to accumulate in these areas, leading to edema which could lead to other serious health problems. By turning and repositioning patients, nurses can help reduce this swelling, making the patient more comfortable and reducing the risk of further complications.
Proper digestive function is another bonus. When patients lie in one position for a long time, their digestive system can slow down, leading to constipation and other gastrointestinal problems. Regular repositioning stimulates digestion and encourages normal bowel function.
Finally, the psychological benefits are huge. Feeling neglected or uncomfortable can make a patient’s mental health worsted. Regularly turning and positioning patients not only provides physical relief but also lets nurses interact with them more frequently. This interaction offers emotional support and can significantly boost the patient’s mental well-being.
Best Practices for Effective Patient Turning and Positioning
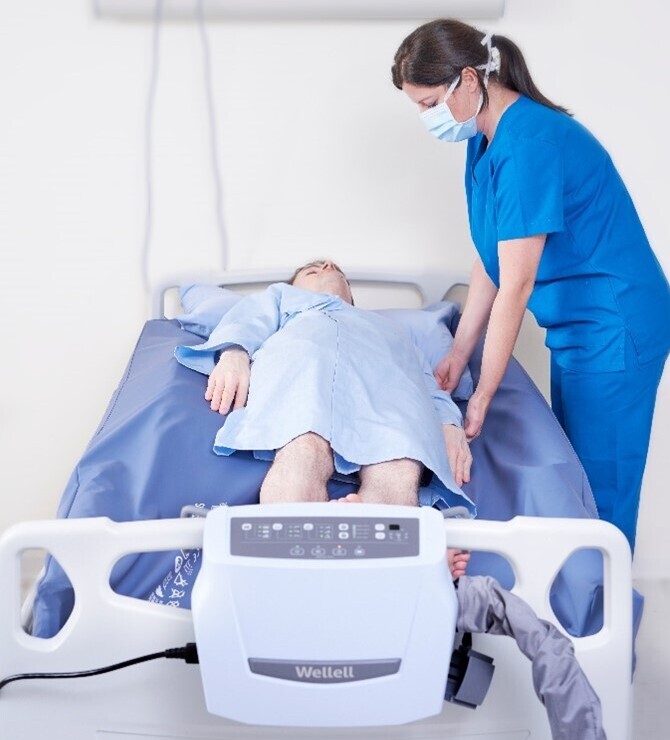 Let talk about the frequency and the best technique to turn and position patients.
Let talk about the frequency and the best technique to turn and position patients.
How often should patients be repositioned? Ideally, aim for every 1 to 2 hours, depending on their condition and specific risks. Consistency is key to prevent issues before they start as bedsores can develop within 1-2 hours when blood circulation stops.
What’s about proper technique? Nurses need to use correct lifting and turning techniques to protect both themselves and the patient. Incorrect methods can lead to injuries and that is what we are trying to avoid.
Supportive equipment is your best friend. Use pillows, wedges, or specialized mattresses to maintain proper alignment and minimize pressure on vulnerable areas. These tools can make a big difference in both comfort and effectiveness.
In conclusion, nurse-patient interaction is essential. This is not only physically moving a person, but also an opportunity to interact, assess their condition, and provide reassurance. This interaction is crucial for their mental well-being.
